Vitaceae
Virginia creeper
Parthenocissus quinquefolia
Synonyms
Hedera quinquefolia
Ampelopsis quinquefolia
Cissus hederacea
Cissus quinquefolia
Parthenocissus quinquefolia var. typica
Psedera quinquefolia
Quinaria hederacea
Quinaria quinquefolia
Vitis quinquefolia
Other Common Names
woodbine
Plant Type
Vine
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
30-50 ft. tall
5-10 ft. wide
Tolerant of
Drought
Inolerant of
Poorly Drained Soil
Propagation
By seed, By cutting, By division, By air-layering
Plant Propagation Notes
Seed requires stratification to germinate. It is easiest to propagate from cuttings or air layering in the fall.
Plant Planting Notes
Can be an aggressive spreader. Do not plant on buildings as the sucker discs can cause damage.
Plants/Diseases
Occasionally, Virginia creeper is affected by beetles, scale, leafhoppers, mildews, leaf spot, wilt, or cankers.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Host plant for butterfly larvae, Fruit/seeds for birds
Leaves
leaves alternate, palmate with five leaflets and serrate margins.
Flowers
Small green to white insignificant flowers on a panicle.
Fruit
Bright blue berry.
Bark
Gray to brown with aerial roots and tendrils.
Toxicity
Fruit is highly toxic and should not be consumed by humans. Some individuals have contact dermises when exposed to the sap.
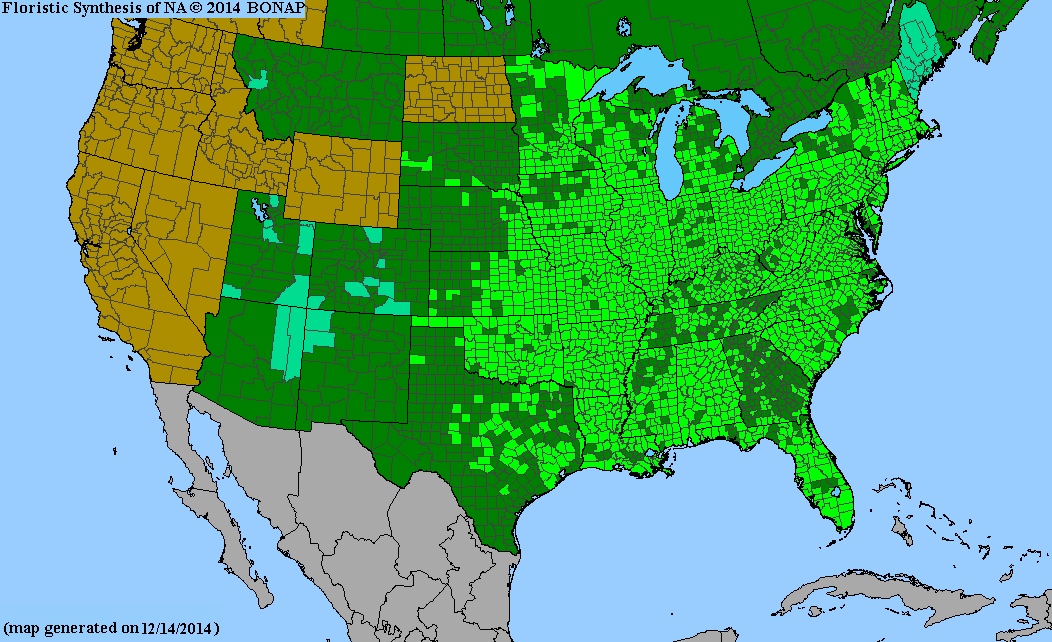
USDA Hardiness Zones
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Light Exposure
Full Sun, Part Sun/Shade
Soil Moisture
Medium, Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0), Neutral (6.0-8.0), Basic (greater than 8.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Forests of swamps, bottomlands, maritime areas. Also grows in mesic forests, thickets, and rock outcrops.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
Distribution Notes
Common throughout South Carolina.




