Magnoliaceae
sweet bay magnolia
Magnolia virginiana
Synonyms
Magnolia virginiana var. australis
Other Common Names
swamp magnolia, sweet bay, small magnolia,
Plant Type
Small Tree/Large Shrub (10-25 ft)
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
12-20 ft. tall
10-20 ft. wide
Tolerant of
Occasional Flooding, Salt Exposure
Inolerant of
Dry Soil
Propagation
By seed, By cutting
Plant Propagation Notes
Cold moist stratify seeds for 60 days. Cuttings can be taken from semi-hardwood in summer.
Plant Planting Notes
Provide up to 20 ft spacing.
Plants/Diseases
May become chlorotic in alkaline soils. Occasionally infested by scale or weevils. Moderately susceptible to leaf spot.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Host plant for butterfly larvae, Fruit/seeds for birds
Leaves
Leaves alternate, elliptical, lanceolate, or oblong with entire margins. Undersides of leaves are silver/green.
Flowers
Three inch, white solitary flowers that are cup-shaped and fragrant with 9-12 petals.
Fruit
Bright red aggregate fruits.
Bark
Bark is light brown to light gray with a smooth surface.
Toxicity
No known toxicity.
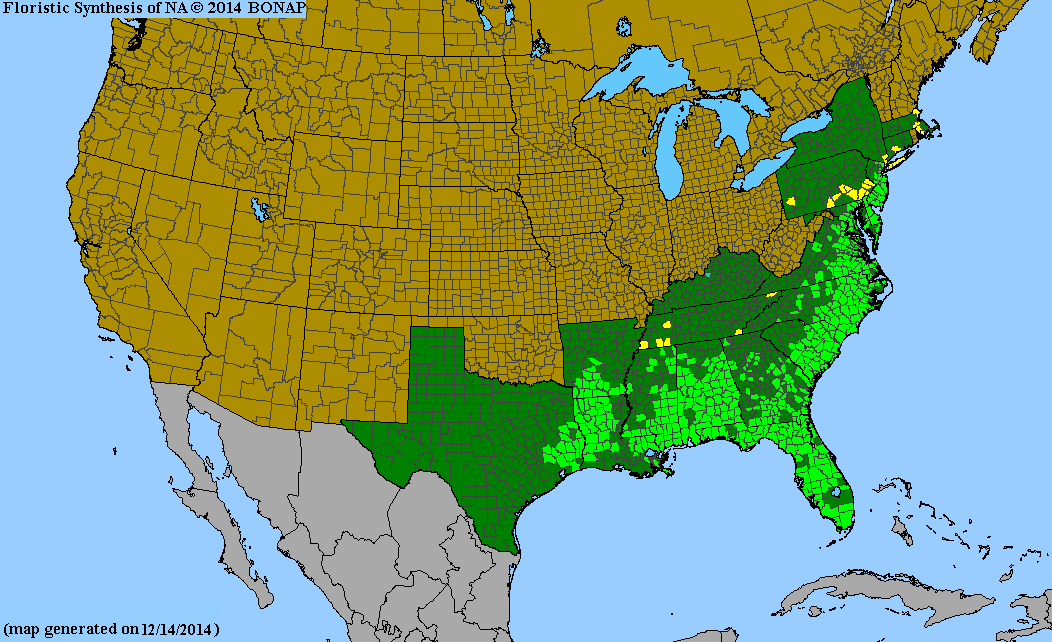
USDA Hardiness Zones
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Light Exposure
Full Sun, Part Sun/Shade
Soil Moisture
Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained, Poorly Drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Wet habitats such as bay forests, pocosins, and swamps.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
Distribution Notes
Common in the South Carolina coastal plain and sandhills. Uncommon to rare in the piedmont. Absent from the mountains.
Subspecies
Magnolia virginiana var. australis
Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana



