Magnoliaceae
southern magnolia
Magnolia grandiflora
Synonyms
Magnolia foetida
Magnolia angustifolia
Magnolia elliptica
Other Common Names
big bay, large tree magnolia
Plant Type
Large Tree (greater than 25 ft)
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
60-80 ft. tall
20-40 ft. wide
Tolerant of
Deer, Occasional Flooding, Salt Exposure
Propagation
By seed, By cutting
Plant Propagation Notes
Seed requires cold moist stratification for 60 days.
Plant Planting Notes
Provide up to 40 ft spacing. In full sun, southern magnolia maintains it’s branches almost to the ground creating dense shade and making underplanting challenging.
Plants/Diseases
Scale sometimes affects the leaves.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Fruit/seeds for birds
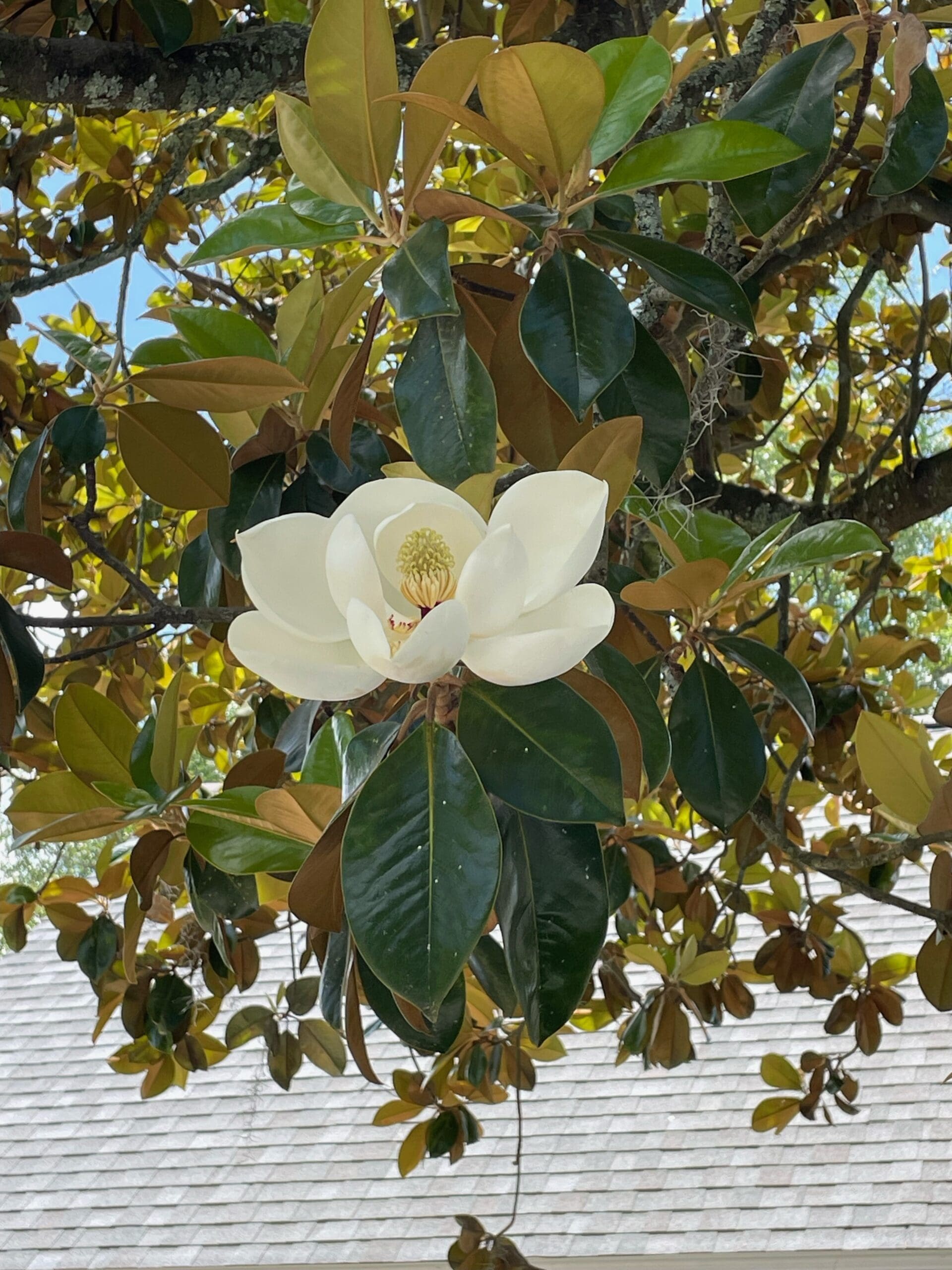
Leaves
Leaves alternate, elliptical to ovate with entire margins. Waxy and deep green on the top, bronze and hairy on the undersides.
Flowers
Large white, solitary flowers that are cup-shaped, fragrant with 6 petals.
Fruit
Bright red fruits in aggregate.
Bark
Dark gray to dark brown smooth when young and develops plates and scales with age.
Toxicity
No known toxicity.
Edibility
Flowers and fruit are edible.
Ethnobotanical Use
Wood is used in furniture, doors, and other woodworking.
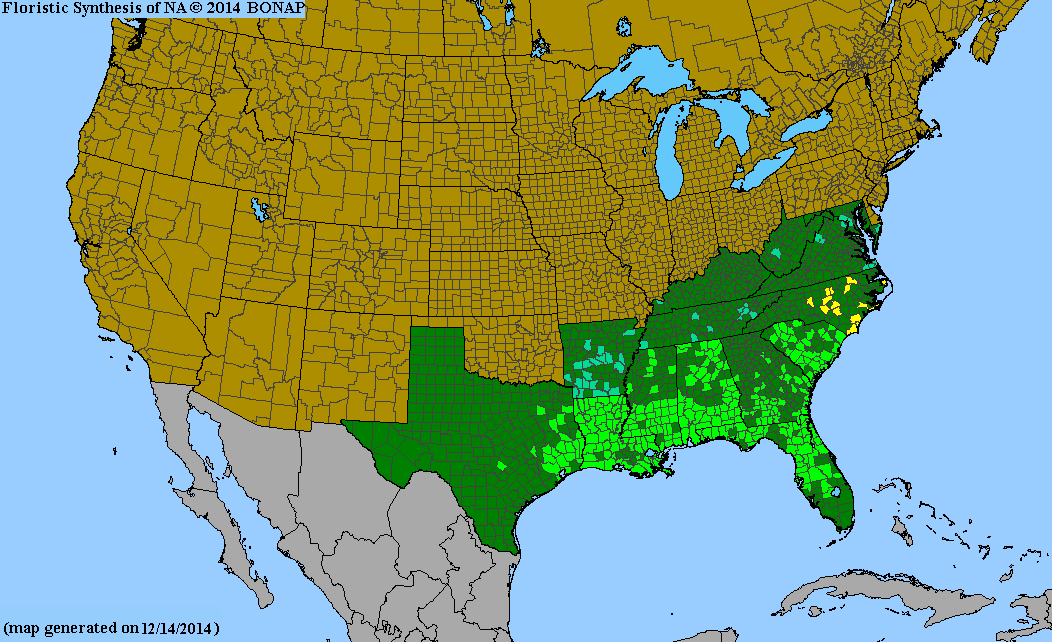
USDA Hardiness Zones
6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Light Exposure
Full Sun, Part Sun/Shade
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0), Neutral (6.0-8.0), Basic (greater than 8.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Bottomland forests, maritime forests, and sometimes dry forests escaping from cultivation.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
Distribution Notes
Common in the South Carolina coastal plain and sandhills. Introduced to the piedmont and mountains.





