Caprifoliaceae
coral honeysuckle
Lonicera sempervirens
Synonyms
Caprifolium sempervirens
Periclymenum sempervirens
Phenianthus sempervirens
Other Common Names
honeysuckle, trumpet honeysuckle, woodbine
Plant Type
Vine
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
10-20 ft. tall
3-6 ft. wide
Tolerant of
Occasional Flooding
Inolerant of
Dry Soil
Propagation
By seed, By cutting, By air-layering
Plant Propagation Notes
Cold moist stratify seed for 60-90 days. Cuttings can be made from softwood or semi-hardwood cuttings taken in summer to fall.
Plant Planting Notes
Coral honeysuckle is a twining vine that requires some kind of support structure to grow on such as a trellis or fence.
Plants/Diseases
Coral honeysuckle may experience leaf spot or powdery mildew, especially in hot and humid weather. Aphids are occasional pests.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Nectar source for hummingbirds
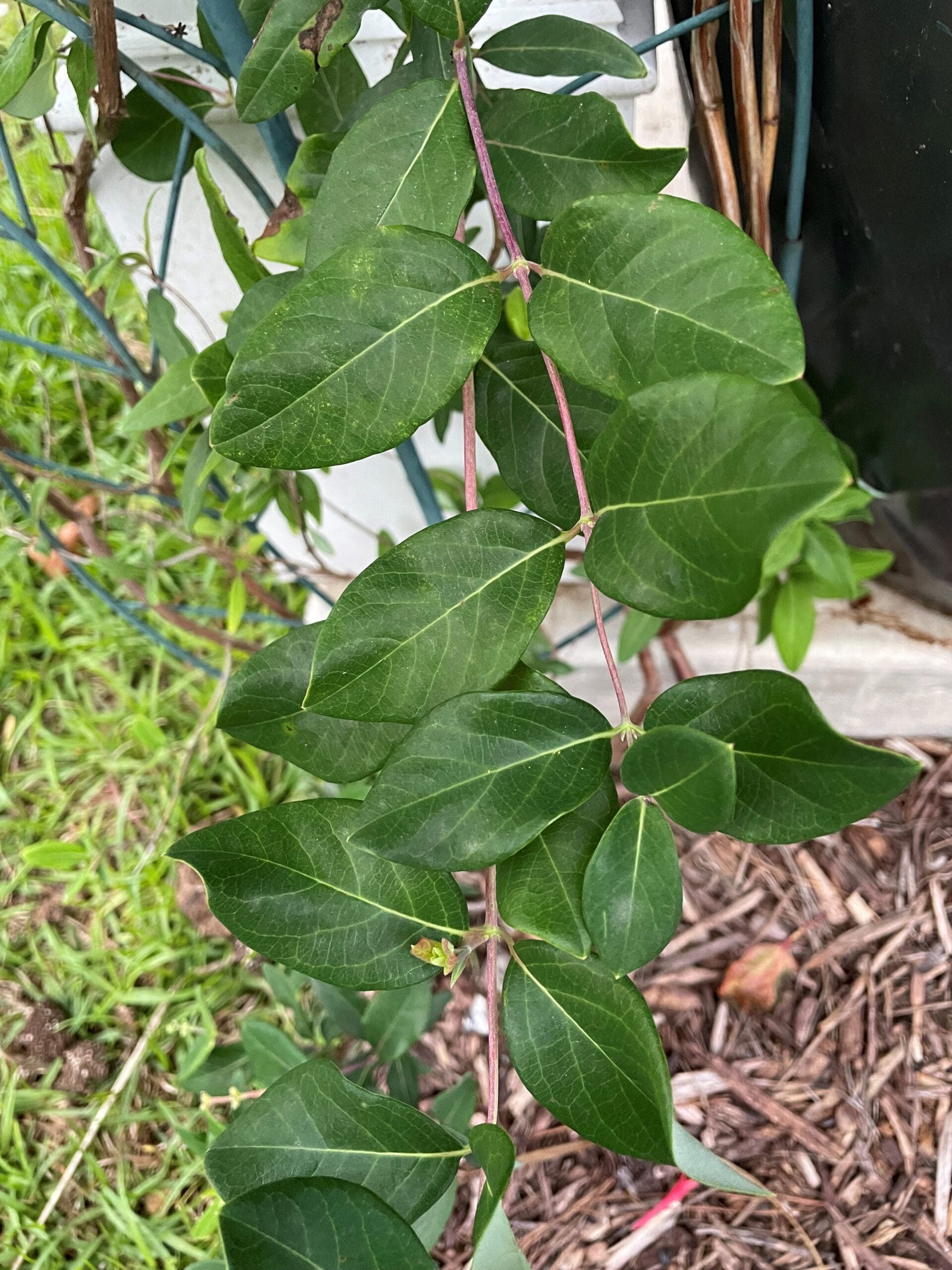
Leaves
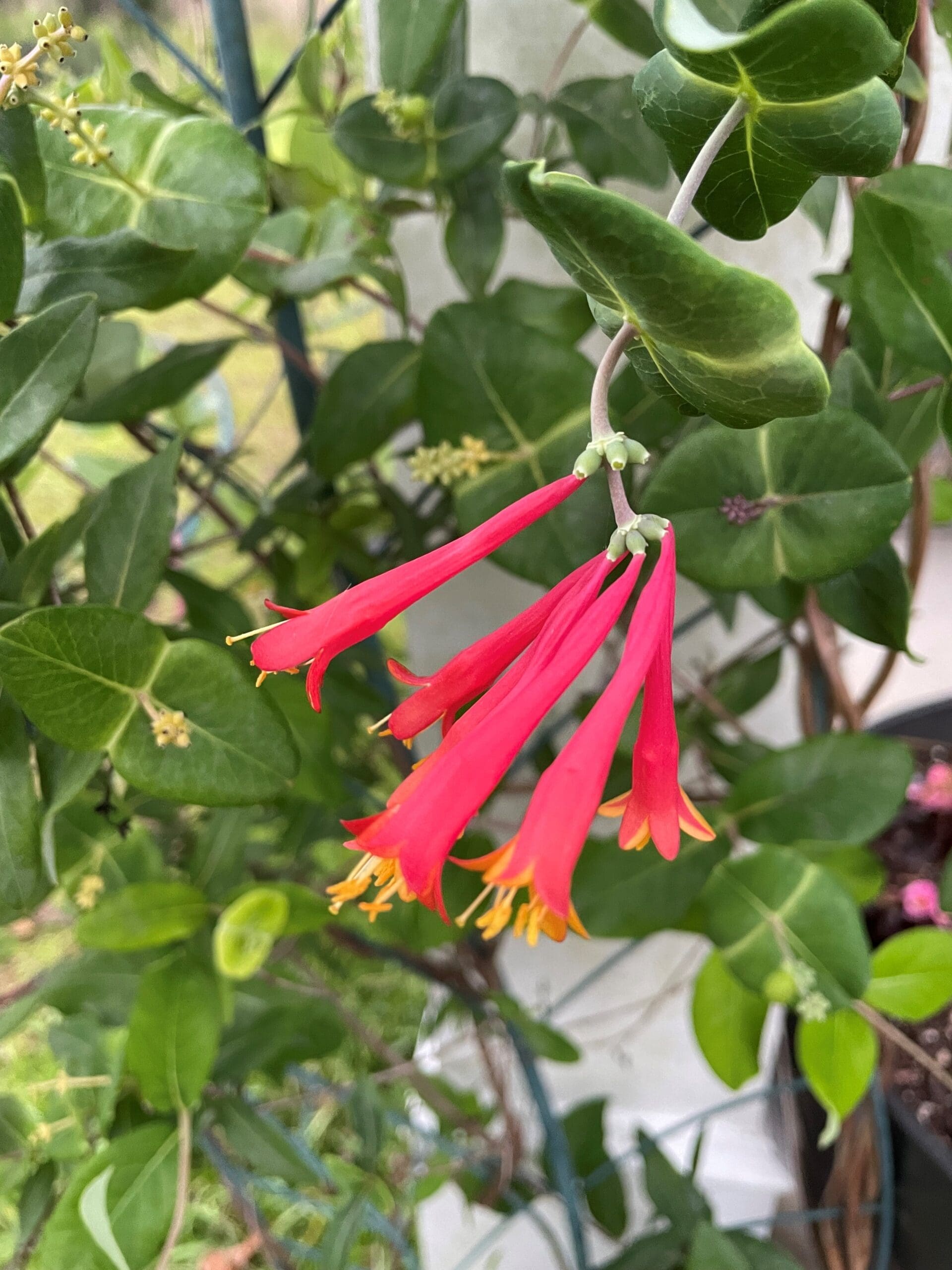
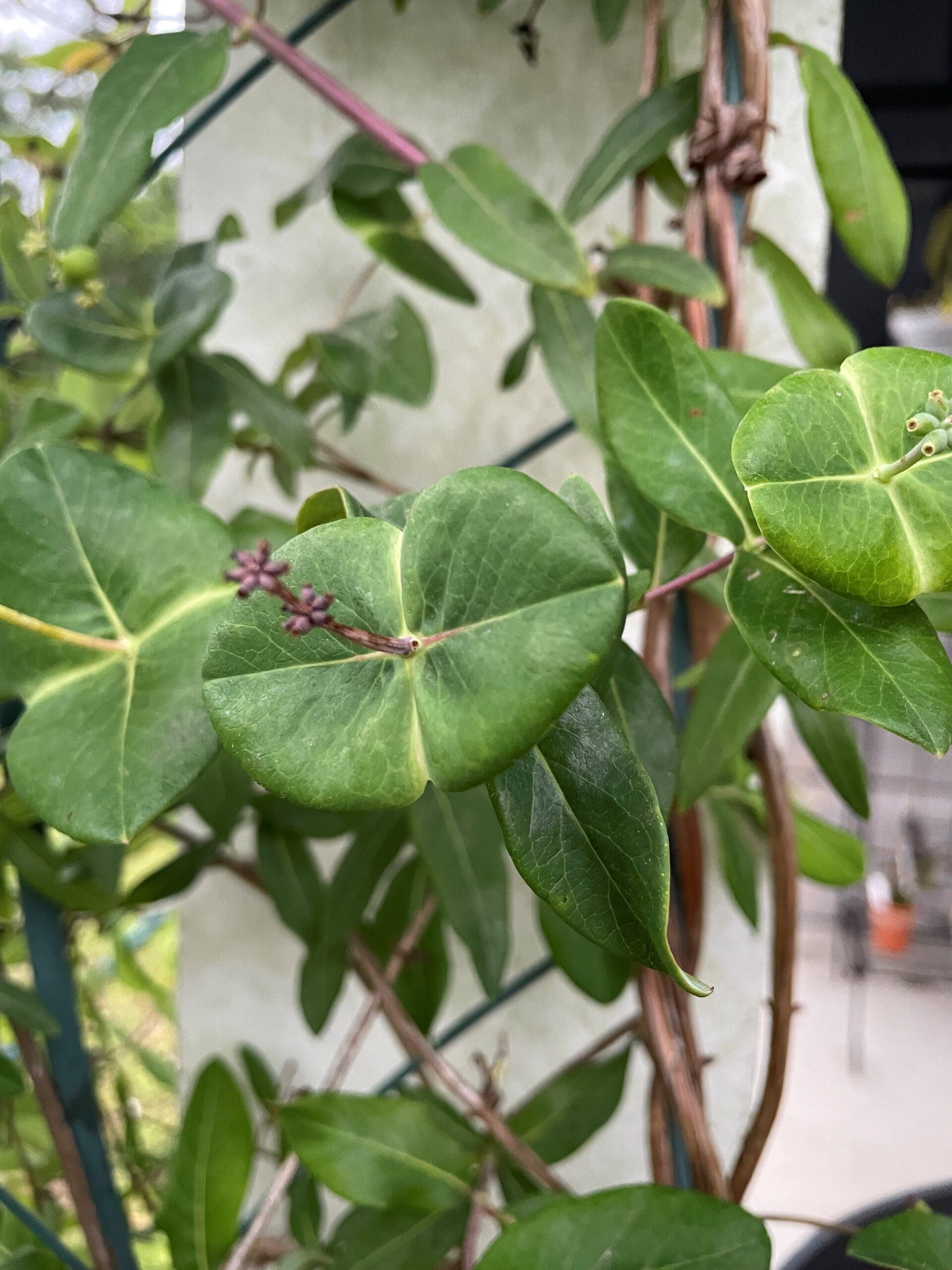
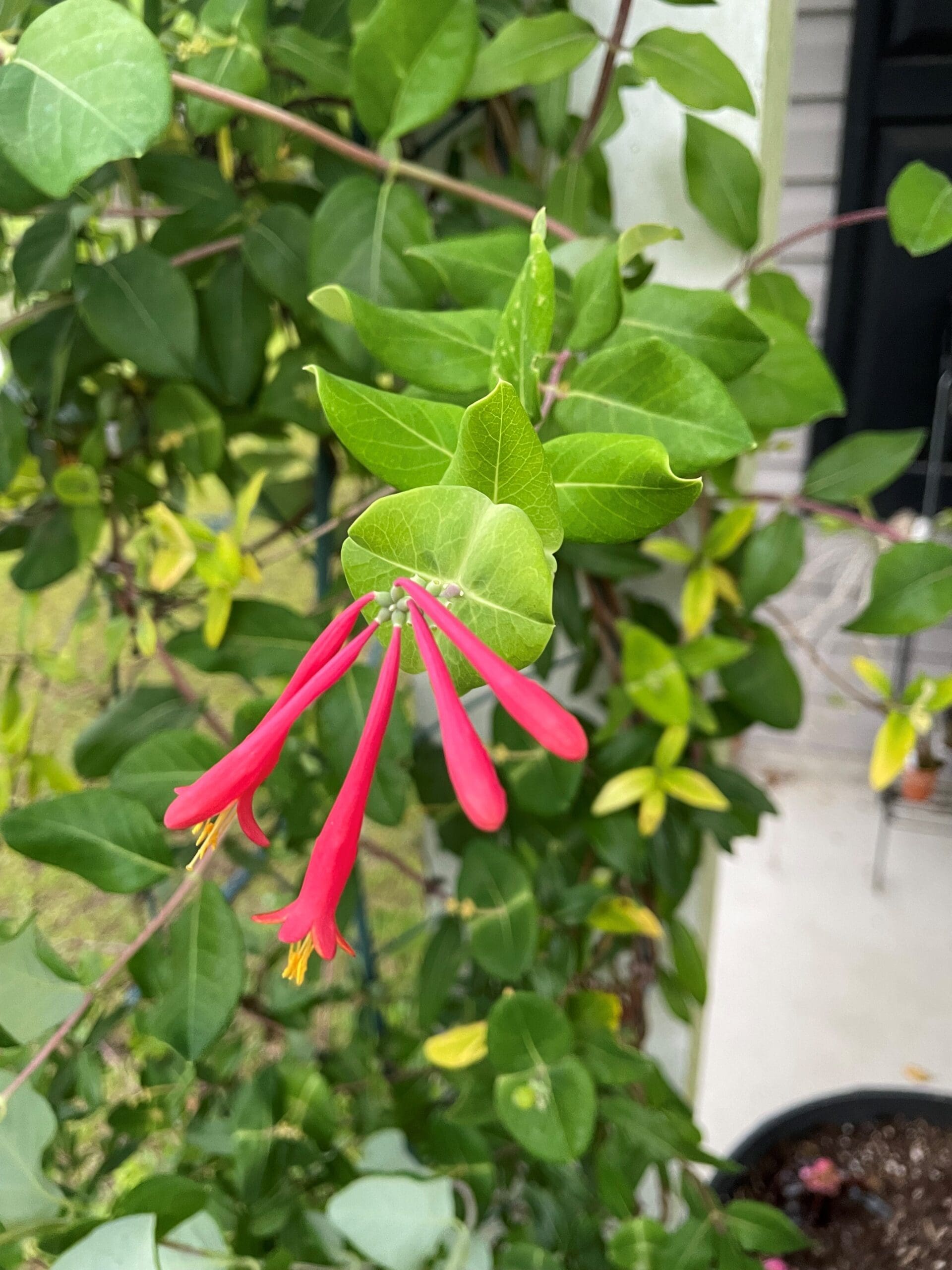
Leaves opposite, oblong to ovate with entire margins. Leaves that produce inflorescences are perfoliate (fused together).
Flowers
Spikes of tube-shaped flowers with bright red on the outside and bright yellow on the inside.
Fruit
Red berries turn to black when mature.
Bark
Older growth develops a light brown bark that exfoliates.
Toxicity
No known toxicity.
Ethnobotanical Use
Leaves were dried and historically used for asthma, bee stings, and sore throats.
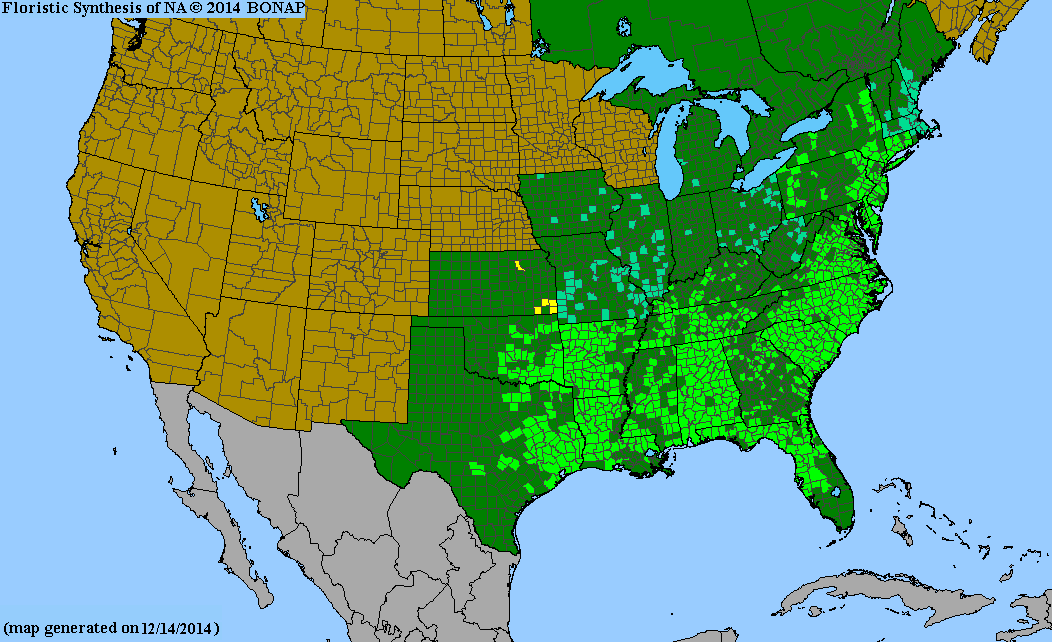
USDA Hardiness Zones
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Light Exposure
Full Sun, Part Sun/Shade
Soil Moisture
Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0), Neutral (6.0-8.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Forests and woodlands and maritime forests.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
Distribution Notes
Common throughout South Carolina.






