Styracaceae
common silverbell
Halesia tetraptera
Synonyms
Halesia carolina
Halesia monticola
Other Common Names
mountain silverbell
Plant Type
Large Tree (greater than 25 ft)
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
10-40 ft. tall
25-35 ft. wide
Inolerant of
Dry Soil, Poorly Drained Soil
Propagation
By seed, By cutting
Plant Propagation Notes
Seeds need a warm moist stratification followed by a cold moist stratification and may still take up to two years to germinate, but will usually germinate within weeks. Root cuttings and softwood cuttings can be rooted for propagation.
Plant Planting Notes
Provide up to 35 ft spacing.
Plants/Diseases
Leaves can become chlorotic in soils that are too alkaline.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Host plant for butterfly larvae, Fruit/seeds for birds, Supports numerous caterpillars (bird food)
Leaves
Leaves alternate, oblong to ovate with dentate to serrate margins.
Flowers
Mainly white, sometimes pink, bell-shaped flowers.
Fruit
Drupe.
Bark
Young twigs are brown and smooth. Older bark forms scaling plates.
Toxicity
No know toxicity.
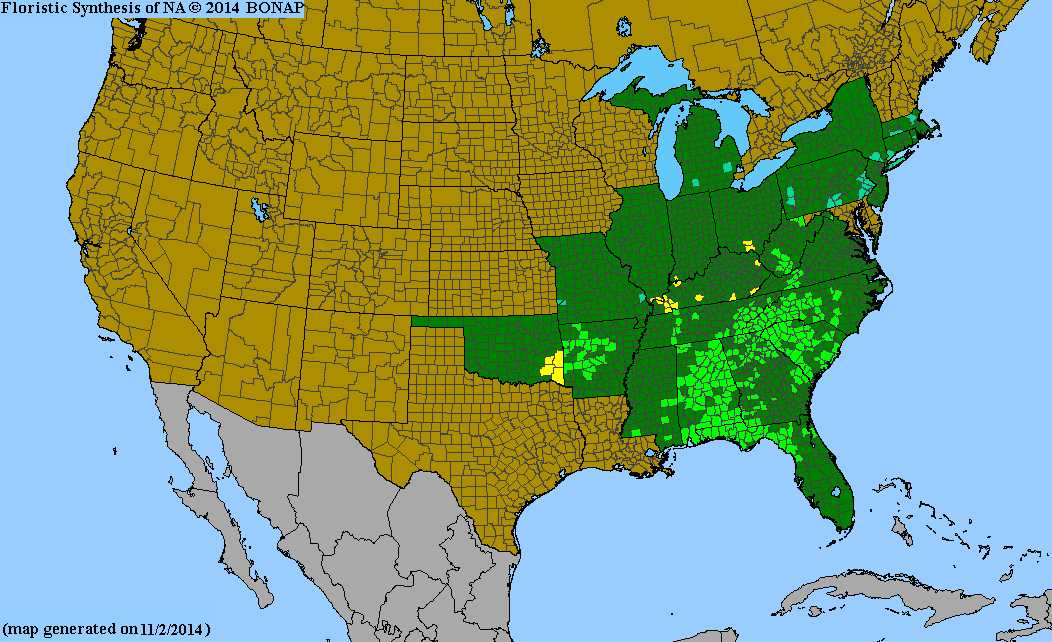
USDA Hardiness Zones
4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Light Exposure
Full Sun, Part Sun/Shade
Soil Moisture
Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0), Neutral (6.0-8.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Bottomlands, slopes, and creek banks with moist soils.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
Distribution Notes
Uncommon in South Carolina coastal plain, sandhills, and piedmont. Common in the mountains.
Subspecies
Halesia tetraptera var. tetraptera
Halesia tetraptera var. monticola





