Betulaceae
American hazelnut
Corylus americana
Synonyms
Corylus americana var. americana
Corylus americana var. indehiscens
Other Common Names
American filbert
Plant Type
Small Tree/Large Shrub (10-25 ft)
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
9-12 ft. tall
8-13 ft. wide
Inolerant of
Poorly Drained Soil
Propagation
By seed, By cutting
Plant Propagation Notes
Use softwood cuttings. Rooting of cuttings is typically low. Nuts should be cold moist stratified for at least a couple of months and take a long time to germinate.
Plant Planting Notes
Several plants allow for cross pollination and better fruit set. Full sun will also result in higher fruit set than part shade. It is not salt tolerant.
Plants/Diseases
Minor issues include Japanese beetles, scale, leafhoppers, leaf spots, blight, and crown gall.
Wildlife Benefits
Host plant for butterfly larvae, Fruit/seeds for birds
Leaves
Leaves alternate, elliptical to ovate with doubly serrated margins.
Flowers
Plants have separate male and female flowers. Female flowers bloom in clusters within a swollen bud only showing red stigmas. Male flowers are yellow to brown on long catkins.
Fruit
Nut enclosed in two protective bracts.
Bark
New growth is smooth and gray. Older growth becomes more rough.
Toxicity
No known toxicity.
Edibility
The nuts are edible. Often roasted and eaten or ground into a flour.
USDA Hardiness Zones
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Light Exposure
Full Sun, Part Sun/Shade
Soil Moisture
Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0), Neutral (6.0-8.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Forests and woodlands with mesic, rocky soils as well as rich forests and thickets.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
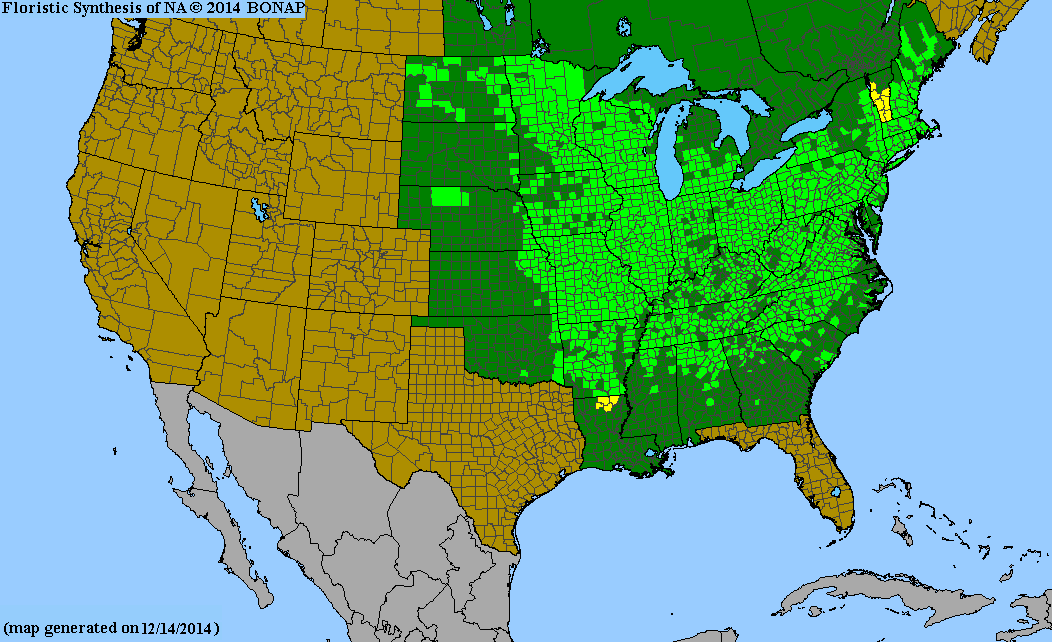
Distribution Notes
Rare in the South Carolina coastal plain and sandhills. Common in the piedmont. Uncommon in the mountains.




