Nyssaceae
black tupelo
Nyssa sylvatica
Synonyms
Nyssa multiflora var. sylvatica
Nyssa sylvatica var. typica
Other Common Names
blackgum, black tupelo, common tupelo, cotton gum, pepperidge, sour gum
Plant Type
Large Tree (greater than 25 ft)
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
40-70 ft. tall
20-35 ft. wide
Tolerant of
Drought, Occasional Flooding
Inolerant of
Poorly Drained Soil
Propagation
By seed
Plant Propagation Notes
Once the fruit pulp has been removed, cold moist stratify for 30-60 days.
Plant Planting Notes
Black tupelo trees forma deep taproot, so are not easily transplanted.
Plants/Diseases
Insects that may affect black tupelo trees are leaf miners and scale. Trees are susceptible to leaf spot, cankers, and rust.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Fruit/seeds for birds
Leaves
Leaves alternate, elliptical to obovate with entire to dentate margins; thick cuticle.
Flowers
Small white to green flowers in umbels.
Fruit
Drupe.
Bark
Dark brown to gray with deep furrows and square or rectangle bark plates.
Toxicity
No known toxicity.
Edibility
Fruits are edible.
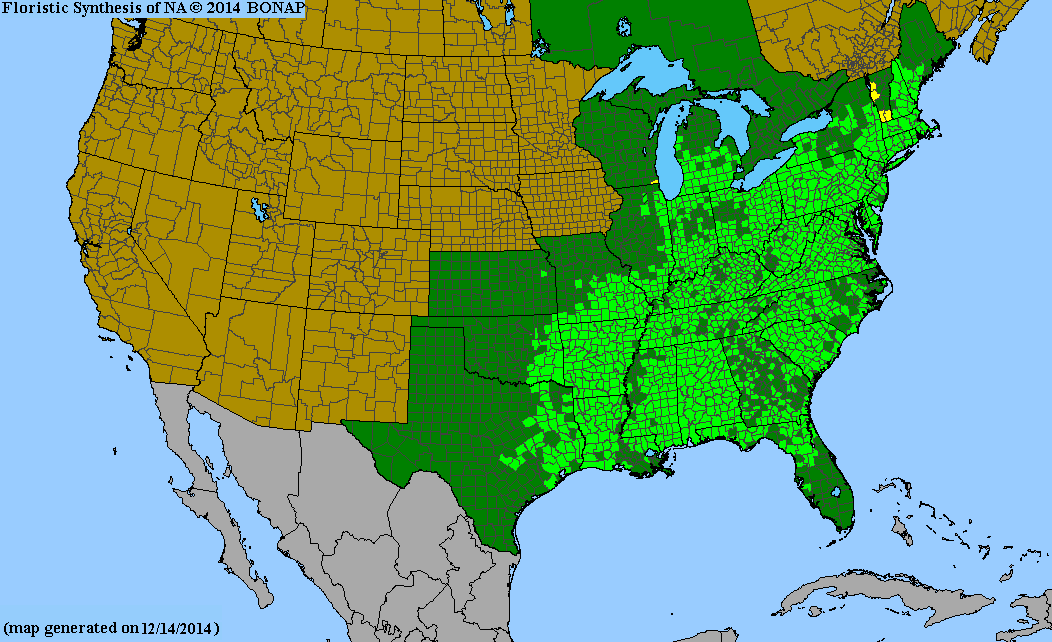
USDA Hardiness Zones
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Light Exposure
Full Sun
Soil Moisture
Dry, Medium, Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0), Neutral (6.0-8.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Upland forests with xeric to mesic soils. Occasionally found in bottomlands or pine savannahs.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
Distribution Notes
Common throughout South Carolina.




