Ericaceae
great laurel
Rhododendron maximum
Other Common Names
white rosebay, great rhododenron
Plant Type
Small Tree/Large Shrub (10-25 ft)
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
5-15 ft. tall
5-12 ft. wide
Inolerant of
Direct Afternoon Sun
Propagation
By seed
Plant Propagation Notes
No pretreatment is necessary. The best temperature range for germination is between 45-50 degrees.
Plant Planting Notes
Provide up to 12 ft spacing. Pruning should be done after flowering.
Plants/Diseases
A number of insects may inhabit great laurel including aphids, borers, lace bugs, leafhoppers, mealybugs, mites, nematodes, scale, thrips, and white fly. Disease that affect great laurel include canker, crown rot, leaf spot, rust, and powdery mildew. Root rot may occur in poorly drained soils.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Nectar source for hummingbirds
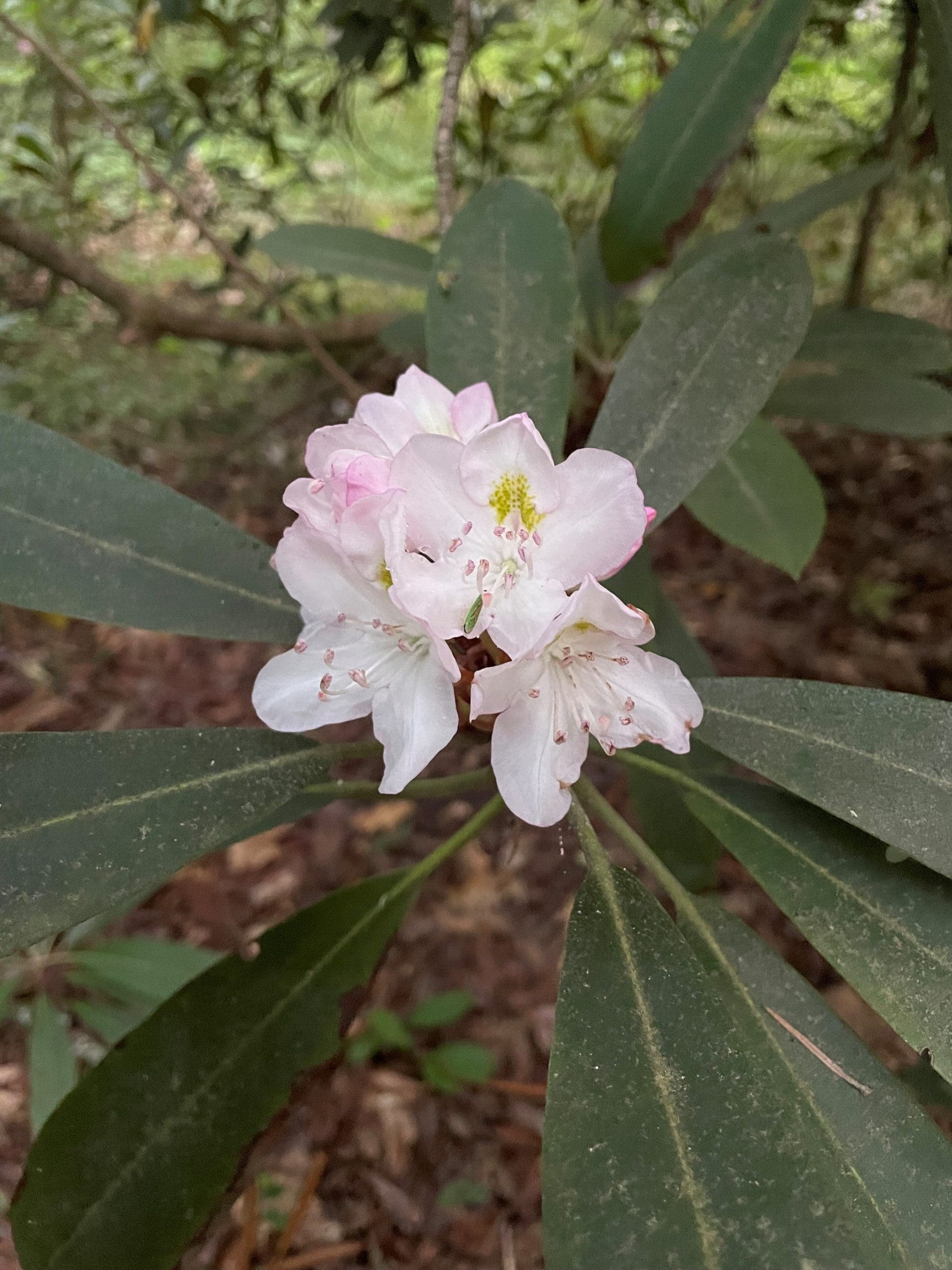
Leaves
Leaves alternate, simple and smooth with a leathery texture; margins entire. Leaves greater than 6 inches long.
Flowers
Large showy funnel-shaped flowers on a raceme.
Fruit
Capsule.
Bark
Light brown bark is smooth when young and develops thin scales as the plant ages.
Toxicity
All parts of the plant are highly toxic if consumed, even in small amounts.
USDA Hardiness Zones
3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Light Exposure
Part Sun/Shade, Full Shade
Soil Moisture
Medium, Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
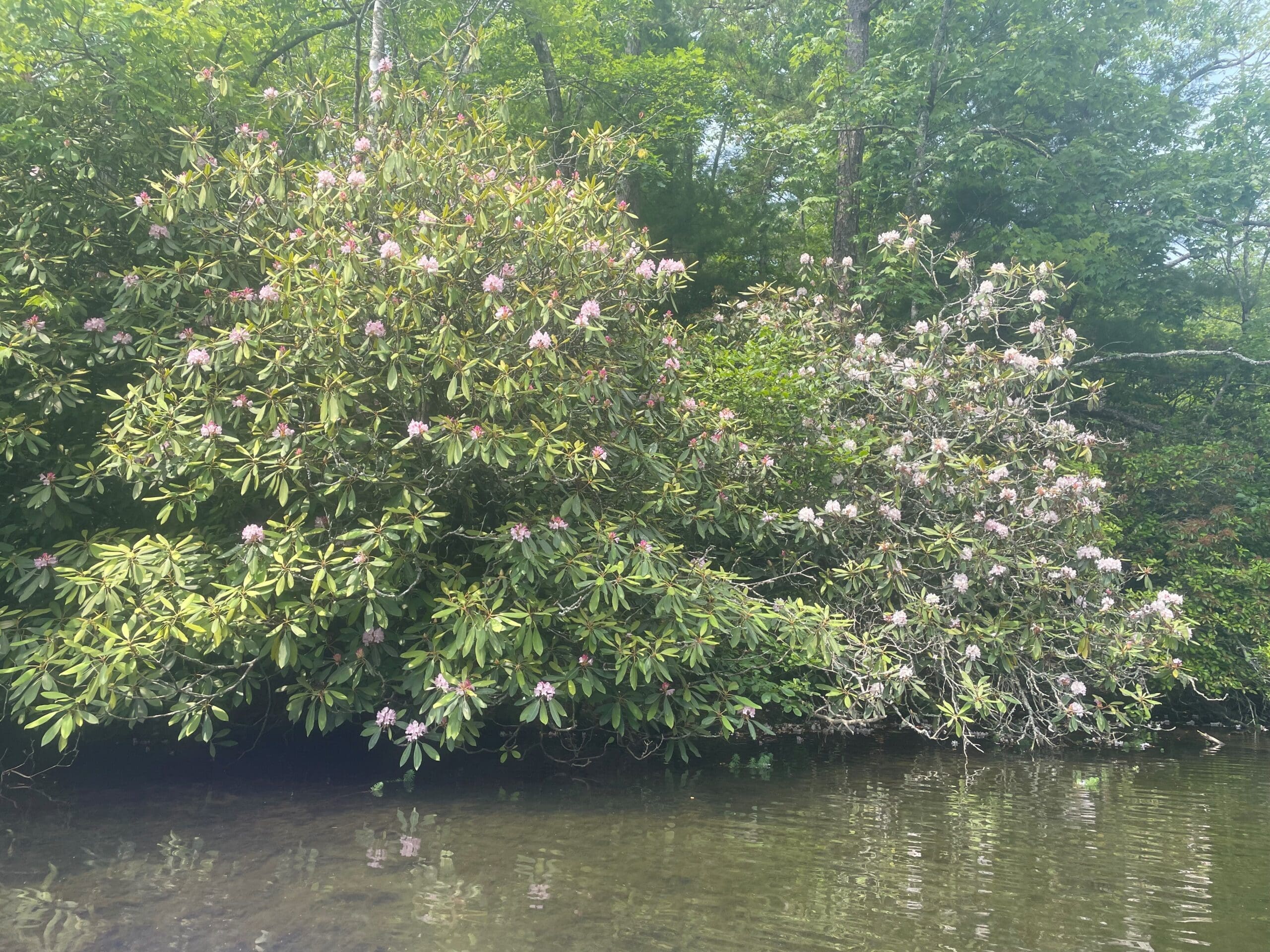
Plant Native Habitat
North-facing bluffs in the piedmont region as well as moist slopes and other acidic moist environments in the mountains.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
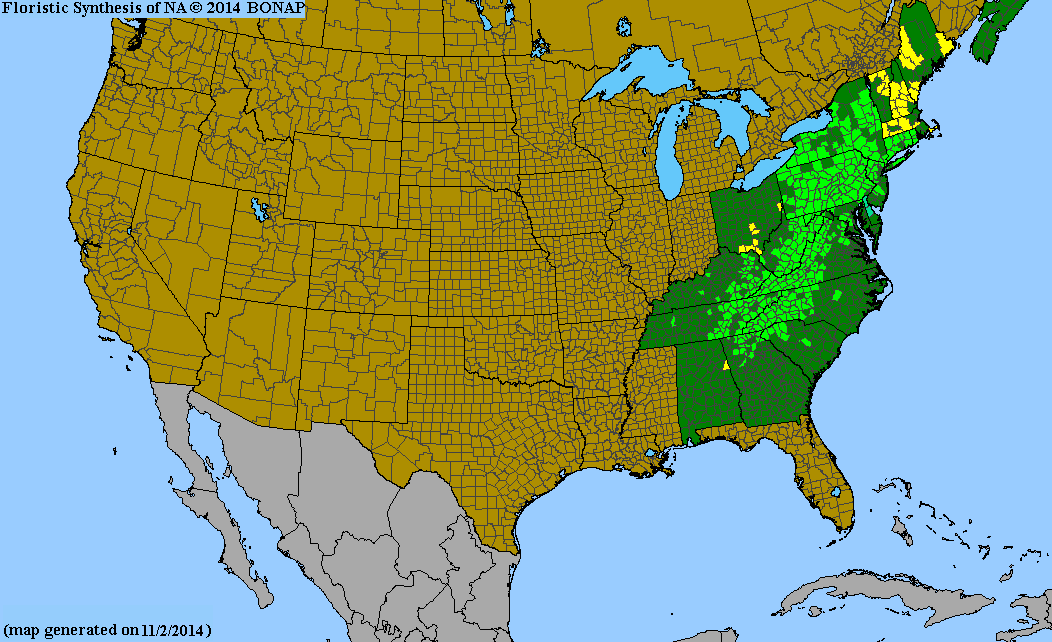
Distribution Notes
Absent from the South Carolina coastal plain and sandhills. Uncommon in the piedmont. Common in the mountains.




