Hamamelidaceae
witch-hazel
Hamamelis virginiana
Synonyms
Trilopus virginiana
Other Common Names
common witchhazel
Plant Type
Small Tree/Large Shrub (10-25 ft)
Life Cycle
Perennial
Typical Size
8-25 ft. tall
Tolerant of
Occasional Flooding
Inolerant of
Dry Soil
Propagation
By air-layering
Plant Propagation Notes
Seed requires double stratification; warm stratification for 60 days followed by cold, moist stratification for 90 days.
Plants/Diseases
No serious disease or insect issues. Occasionally insect galls appear on foliage, but do not affect the overall health of the plant. Watch for Japanese beetles. Powdery mildew or leaf spots may appear on the leaves.
Wildlife Benefits
Nectar/pollen source for pollinating insects, Fruit/seeds for birds
Leaves
Leaves alternate. Leaf blade broad-elliptic to nearly rounded with dentate margins. Leaf base strongly oblique. Approximately 3-6 inches long.
Flowers
Yellow spidery looking flowers with 4-5 petals, approximately 1 inch wide.
Fruit
Capsules with two black seeds.
Bark
Young stems zig-zag.
Toxicity
No known toxicity.
Ethnobotanical Use
Witch hazel extract has long been used medicinally as an astringent.
USDA Hardiness Zones
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Light Exposure
Full Sun, Part Sun/Shade
Soil Moisture
Moist
Soil Drainage
Well-drained
Soil pH
Acidic (less than 6.0)
Native in South Carolina?
Yes
Plant Native Habitat
Dry woodland slopes, moist woods, bluffs, and high hammocks.
Global Conservation Status (NatureServe)
Secure (G5)
Federal Conservation Status (USFWS)
Not Listed
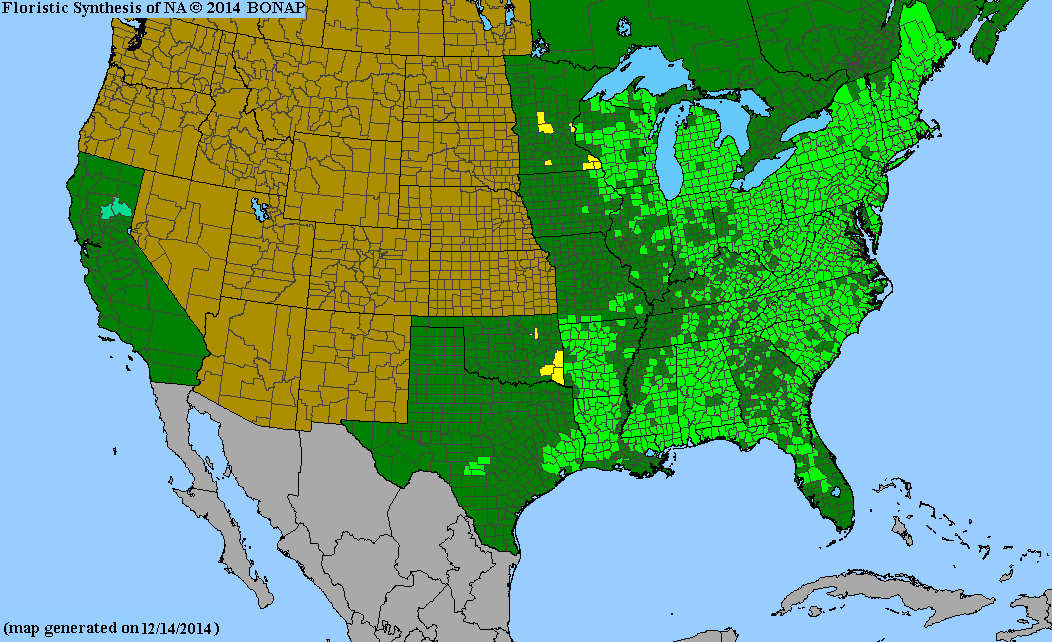
Distribution Notes
Common throughout South Carolina




